
Specifications for packaging materials
Excerpt form the GMP Series – Packaging Materials for Pharmaceutical Products
5 min. reading time | by Roland Kleissendorf
Published in LOGFILE 15/2021
A correctly formulated packaging material specification provides a comprehensive description of the packaging material and serves as a guideline for the respective packaging materials supplier.
In addition, it forms the basis for quality testing at the packaging materials suppliers and for the incoming control at the medicinal product manufacturer.
Particular significance attaches to the correct allocation of all packaging material specifications and printed information (batch number, expiry date, price) in a bill of packaging materials for the packaging plant.
It is obviously necessary to entrust highly qualified people with the coordination and compilation of these specifications and documents. In the case of packaging material ranges comprising 1,000 and more individual components, an IT-supported approach is needed.
Because important packaging material requirements depend on the packaging process and the machines used, the persons responsible for the packaging materials specification are normally located in or around production. The packaging material guidelines and packaging instructions required for packaging must be authorised and available in written form because they are also needed for the release by the person in charge of QC. These instructions are mainly technical instructions and must also include the printing instructions for the respective packaging materials. This is normally a PDF file created using DTP software. The specifications of the packaging materials manufacturer and logistics/purchasing are also required for an adequate packaging materials specification.
Depending on the medicinal product range for packaging, a change frequency of three to four changes per year must be expected, especially in the case of printed packaging materials such as instructions for use and folding cartons. The creation of packaging material specifications requires a clear and robust process, which can also handle an extremely short-term scope of change without any problems.
The contents of the packaging materials specification for primary packaging materials are generally already specified in the documentation of the pharmaceutical technology, and as a result, in the registration documentation of the medicinal product. The number of products to be packaged, i.e. the content of the package, depends on the length of time the medicinal product is normally taken.
A suitable packaging machine is then selected on the basis of these specifications. The standards (e.g. the dimensions of the packaging) of this machine are also required for the packaging material specification.
In many cases the packaging and/or packaging material manufacturer’s data sheets (e.g. paper and paperboard specifications, glue types in the case of adhesive labels) can also be made available. They contain key parameters for the packaging process, which can be carried over. Data sheets can also be cross-referenced if they are clearly identified, i.e. using the publishing date.
There are also industrial standards in many areas (DIN, EN and ISO standards) that can be used as an excellent basis for packaging material specifications.
Country-specific standards (font size, amount of text, use of colours, etc.) now have a considerable influence on the dimensions and design of printed packaging material (blister packs, labels, package inserts and folding cartons). In some cases different packaging techniques have to be used (e.g. an unfolded package insert becomes a multiple-fold insert or outsert). This again affects the choice of packaging technology.
Additional requirements from the areas of logistics (such as delivery times) and purchasing (conditions) are generally included in the packaging material specifications.
In order to ensure the uniqueness of a packaging material, multi-digit packaging numbers are assigned, which should be altered with every modification. To prevent any mix-ups between similar types of packaging, visual markers and bar codes or 2D matrix codes are used and monitored by the packaging material manufacturer and during the packaging process.
Some of the characteristics of packaging materials that must be defined in the specification are shown in Figure 13.A-4. The checkpoints are usually monitored and verified during testing of the packaging material by the manufacturer. Particular checkpoints can also be monitored if required during acceptance testing by the manufacturer of the pharmaceutical product.
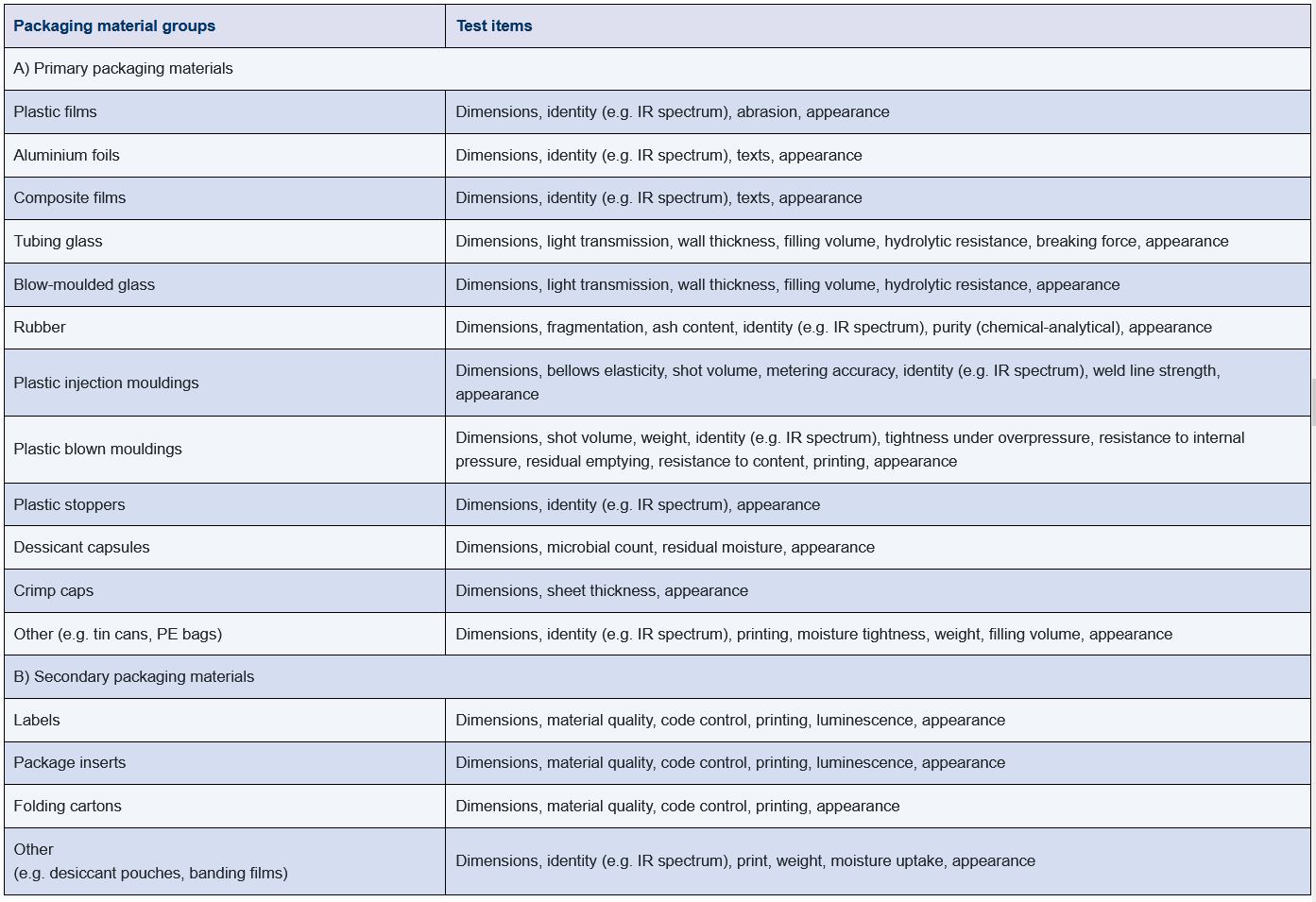
Figure 13.A-4 Packaging material groups with typical tests
Do you have any questions or suggestions? Please contact us at: redaktion@gmp-verlag.de







