
Qualification of Water Supply Systems – Introduction
Excerpt from the GMP Compliance Adviser, Chapter 5.D.1
4 min. reading time | by Fritz Röder
Published in LOGFILE 10/2023
Pharmaceutical water systems are used for a number of different applications by pharmaceutical manufacturers. These include, for example, the cleaning of various pieces of equipment, the generation of pure steam and the use of water as an ingredient for solid, semi-solid and liquid medicinal products.
As a result, an pharmaceutical water system has a significant direct and indirect impact on the quality of the medicinal product which means that qualification is absolutely essential. For technical and inherent reasons, the qualification of a water supply system can be a lot more complex than for other system types. Due to the fact that the quality of drinking water is subject to natural seasonal fluctuations, the qualification phase of a new system takes no less than a year in total. However, the release of water for production can take place earlier.
The qualification is carried out formally in accordance with the model that is used for all other systems:
- Design qualification (DQ)
- Installation qualification (IQ)
- Operational qualification (OQ)
- Performance qualification (PQ)
The basis for each qualification phase is a risk analysis and a qualification plan in which the test points are specified. A report is created based on the plan, and the results of the tests carried out are entered in this report. The approved report completes the qualification phase.
In practice, an "integrated qualification" can increasingly be observed, i.e. the com bination of commissioning and qualification (C & Q). The concept follows ASTM E2500-13 and focuses on the subject matter experts involved. The result is that duplicate tests are avoided in the context of C & Q. Already during the factory acceptance test (FAT) and the site acceptance test (SAT) certain qualification tests can be performed. This concept is also applicable and useful for water systems.
Qualification and commissioning
Only the GMP-relevant aspects of the water supply system require qualification. There are also other aspects of a water supply system that are not GMP-relevant, but must be tested nevertheless, e. g. compliance with the requirements of the machinery directive. This is done during commissioning. As can be seen in figure 1, qualification and com-missioning are normally carried out simultaneously.
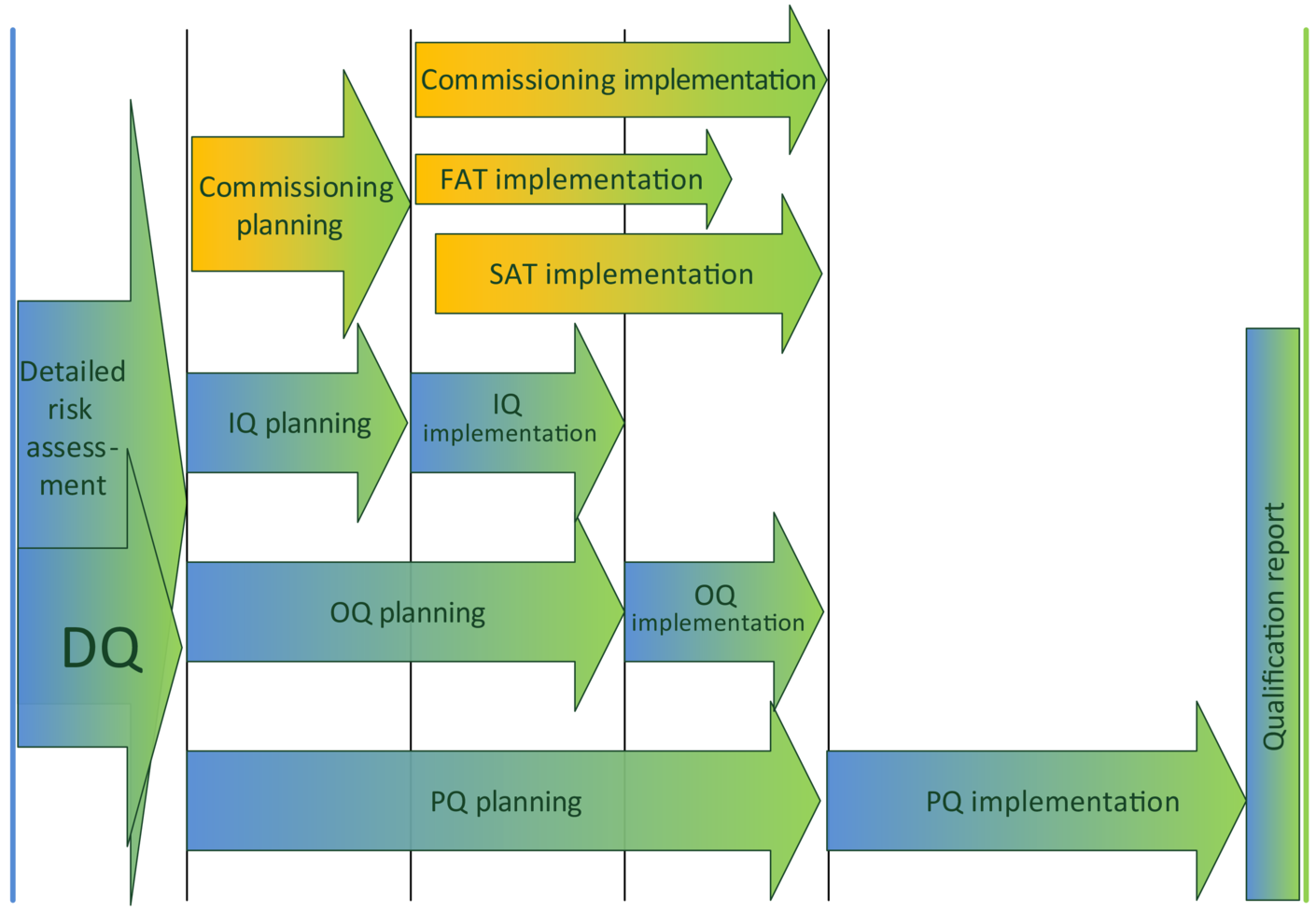
Figure 1 Overlapping of qualification/commissioning
In the schedule for the qualification of water supply systems, the planning and implementation of the different phases always overlap with commissioning activities that are not GMP-relevant. Both phases overlap in terms of content and time, and tests are carried out together if applicable. The "integrated qualification" mentioned at the beginning can save a lot of effort in the further course, but requires good know-how.
Schedule and time required
A buffer should always be factored into the qualification schedule for the following reasons:
- Problems occur during every qualification that need resolving. This takes time.
- Even if the design of water treatment systems is now generally standardised and reproducible, special cases do occur in practice.
- At the end of the different phases of the performance qualification/PQ, the results with regard to the quality of the water must always be acceptable. The microbiological aspects should be looked at most critically. The incubation period of the samples must be observed until a repre-sentative result is obtained.
Be prepared: failed performance qualifications are not uncommon in practic
Therefore, make sure you have a plan B in your project schedule.
The performance qualification is typically divided into three phases. When the first two phases have been successfully completed, the water can be used for pharmaceutical production. In exceptional cases, a release of water "at risk" can also be made after phase one. However, if the action limit is exceeded in phase two, all products manufactured up to that point must be destroyed.
Figure 2 contains an example for a project schedule.
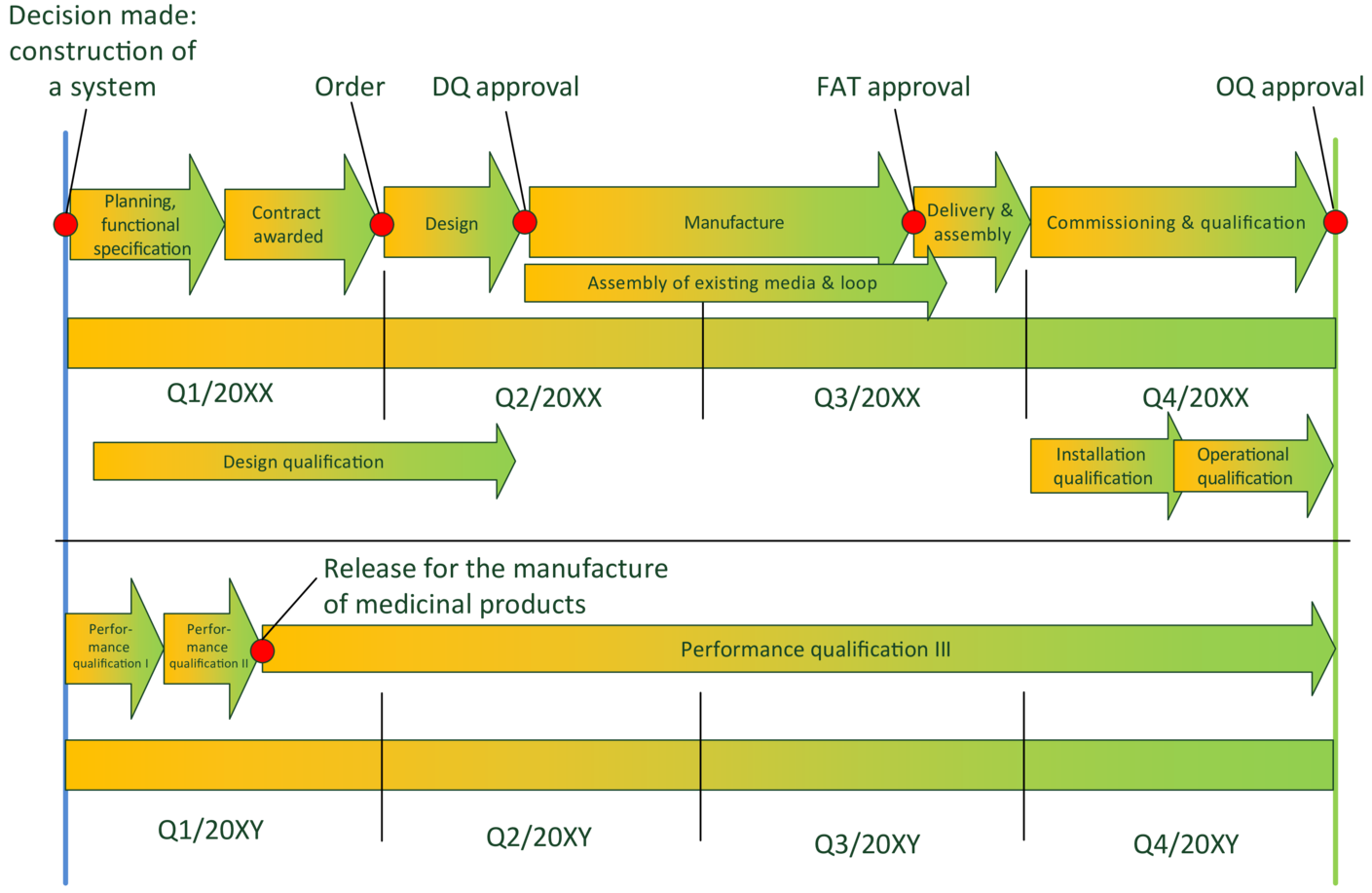
Figure 2 Sample schedule: construction and qualification of an pharmaceutical water system
Scope of the qualification
When qualifying water treatment systems, the parts of the system that should be con-structed from scratch must be considered. The following questions should be asked:
Is an existing system being replaced?
If this is the case, it may be possible to use existing data (product quality review or trend report) to define limits and specifications. If a new site is planned and there has never been a water treatment system there before, calculation formulae must be used. There may be a possibility of using data from nearby water treatment systems for comparative purposes if the same feed water is to be used.
Which parts of the pharmaceutical water system are being replaced?
A distribution loop usually has a longer service life than a production unit. As a result, the parts are frequently replaced at different times. The part that is replaced or changed must be qualified. However, the replacement of one part of the system also affects the other part. Proper consideration (risk assessment) in advance can reduce the scope of the qualification.
When all questions have been answered, the documents can be created. In the case of larger system projects, the creation of a master qualification plan and traceability matrix is required in the interests of providing a better overview. The supplier must also be qualified (in good time).
Water qualities and their uses
The water quality required depends on the dosage form being manufactured and can be taken from the EMA Guideline on the quality of water for pharmaceutical use.
A differentiation in water quality is generally made between "purified water" (PW) and "water for injections" (WFI). The Ph. Eur. and the USP contain a number of further water monographs that take special cases into account.
- Purified Water is generally used for solid dosage forms (e. g. tablets, capsules) and semi-solid medicinal products (ointments).
- When manufacturing parenterals, the use of water for injections is mandatory because the medicinal product is distributed in the bloodstream immediately after injection. The risk to the patient is therefore higher.
Generation
The process of a PW system can be organised in the following way:
- Pre-filtration
- Softening
- Reverse osmosis
- Membrane degassing
- Electro-deionisation (EDI)
- Storage tank and distribution system
Do you have any questions or suggestions? Please contact us at: redaktion@gmp-verlag.de








