
Nothing lasts Forever: Stability Tests are Indispensable
7 min. reading time | by Thomas Peither
Published in LOGFILE 43/2023
The stability of a medicinal product or an active substance is defined as the maintenance of certain quality characteristics (specification) over a fixed period of time under defined conditions.
Stability is only ever given for a limited period of time, as pharmaceutical products change their physical and chemical properties over time.
To protect patients from loss of quality, the extent and rate of these changes must be determined and evaluated through stability studies.
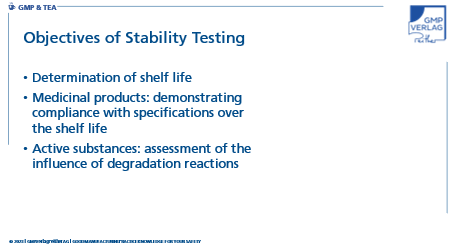
Stability tests are used to determine the shelf life of active substances and medicinal products. In the case of the latter, they are specifically used to demonstrate that they meet the defined specifications over the shelf life. In stability testing of active substances, degradation reactions are of particular interest in order to better assess their influence on the drug formulations.
What are the objectives of stability testing?
To achieve these goals, products are exposed to different primary packaging materials and storage conditions and are subjected to chemical, physical and microbiological testing. The resulting product quality is evaluated holistically at the end of the study.
The results of the stability tests are used to determine the following parameters:
- Test intervals or time to next test
- Hold time of the intermediate product or bulk product
- Shelf life and expiration date
- Storage and transport conditions
What needs to be considered when planning, carrying out and documenting stability studies?
The exact conduct of stability studies must be described in detail in approriate SOPs or work instructions. The first step is the study design, which is set out in a stability protocol.
Particularly towards the end of development activities and in the case of process changes in the market phase, stability testing can take up a considerable amount of time. One way to reduce the scope of testing is to perform long-term storage under harsher conditions, which then covers milder conditions at the same time. However, this approach requires good product knowledge and should be risk based. Another way to reduce the number of tests is to use bracketing and matrixing.
- Bracketing involves testing only the extremes of a product range. For example, if a granulate is filled into different capsule sizes in order to produce different individual doses or strengths, only the lowest and the highest strengths are tested for stability, but the scope of the test remains unchanged.
- Matrixing is used to test a subset of the required samples instead of testing all.
The maximum shelf life of medicinal products is set at five years. However, shorter periods – mostly three years – are often requested.
Minimum requirements apply, as it is not possible to wait the entire duration of the study for regulatory approval. For example, 12 months of results must be submitted for long-term studies and six months for accelerated studies. Submission will normally take place before the end of the study programme of the marketing authorisation batches. The applicant must therefore provide a commitment to continue the stability studies to full completion, specifying the number of batches per year, per strength and packaging material, the test dates and storage conditions to be tested for the full duration of the study, and the scope, parameters and specifications of the tests. Once the medicinal product has been launched, routine annual stability studies must be conducted throughout the marketing period to demonstrate unchanging quality – typically one batch per year per dosage strength level and packaging material.

The results of a stability study shall be summarised in a report, evaluated and subjected to a statistical trend analysis. For registration batches, the stability report including trend analysis and evaluation of the data, shall be included in the application for marketing authorisation. For batches in the marketing phase, the evaluation also takes place within the framework of the PQR. For the data collected, it must be ensured that the technical and practical conditions and the interpretation of the data can be traced back at any time, even after the stability study has been completed. This places high demands on the documentation.
This article is a shortened and translated excerpt from the 36th episode of our German GMP & TEA webcast.
Do you have any questions or suggestions? Please contact us at: redaktion@gmp-verlag.de








