
Import of Medicinal Products – Clarifications in Annex 21
Interpretations of the Irish Health Products Regulatory Authority (HPRA)
10 min. reading time | by Sabine Paris, PhD
Published in LOGFILE 21/2022
The new Annex 21: Importation of medicinal products to the EU GMP Guide has been published on February 21, 2022 and will enter into force on August 21, 2022. The 6-page annex summarises the GMP requirements for Manufacturer/Importer Authorisation (MIA) holders to import medicinal products (human, investigational and veterinary) from outside the EU/EEA.
The Irish Health Products Regulatory Authority (HPRA) hosted a GMP and a GDP conference on May 4-5, 2022. HPRA has published the agendas as well as the presentations on its website. In this article, I have compiled content from the presentation on Annex 21 by Ciara Turley, Senior GMP Inspector at HPRA.
Definition of import in Annex 21
Importation is defined as the action of physically bringing a medicinal product, from outside the territory of EEA/EU; fiscal transactions are not part of Annex 21.
The HPRA points out that financial procurement, supply and export of medicines requires authorisation under a Wholesale Distribution Authorisation (WDA). Financial importation does not require authorisation by the HPRA.
What type of authorisation is required to import?
A Manufacturer/Importer Authorisation (MIA) is required for the importation of medicinal products into the EU.
Die following EU regulations stipulate this:
- Veterinary Regulation 2019/6 Article 88
- Directive for Human Medicinal Products 2001/83/EG Article 40(3)
- Clinical Trial Regulation 536/2014 Article 61
- GDP Guidelines 5.2
Regulatory expectations (not new)
- Imported product must be physically imported before it can be certified by the QP.
- The site where batch certification occurs and the site that physically receives the imported product, if different, requires an MIA.
- Unless there are appropriate arrangements in place between the Union and the third country (e.g. Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA)), it is required to test each batch of product upon importation into the EU before certification by a QP. GMP certificate of laboratory must include testing of imported products
- Annex 16 gives detailed guidance on aspects such as sampling, interconnection of multiple manufacturing sites and QP oversight of the supply chain.
What has Annex 21 clarified?
Importation is considered physical importation and imported products must be customs cleared.
Qualified Person (QP) certification or confirmation, as appropriate, of a batch of a medicinal product takes place only after physical importation and custom clearance into the customs territory of an EU/EEA State.
Scope: Medicinal products that enter the EU/EEA with the intention of export only and that are not processed in any form nor released for placing on the EU/EEA market, are not covered by this Annex.
Examples for import scenarios
Example 1
A product is manufactured in South Africa, transported to the UK, tested in the UK, certified in Ireland and supplied to the UK market.
The product is not imported into the EU. As such the supply chain is outside of the authorised activities of the MIA issued by the HPRA.
Example 2
A medicinal product is manufactured in the EU and the manufacturer holds a MIA. Title to the medicinal product is passed to an entity in a third country but the product remains physically in the EU. An Irish company wishes to acquire title from the entity in the third country.
Would it be possible to apply to the HPRA for an MIA for this activity? The Irish MIA holder also holds a Wholesalers Distribution Authorisation (WDA) in order to facilitate the sale of the medicinal products to other EU entities.
The HPRA does not issue an MIA for financial importation.
Example 3
A medicinal product is manufactured and tested in an EU country before it is exported for secondary packaging to the UK. It re-enters EU for sale and distribution to multiple EU markets. Must the batch be retested after importation into the EU?
Yes, testing on importation would be required if the product has moved outside the EEA for manufacturing activities, including secondary packaging.
Example 4
Products are manufactured in Switzerland. Products are shipped from Switzerland to Germany for the EU. Products are shipped from Germany to all EU markets.
- Will a local QP certification be required in each EU state if the product has already been QP released in Germany?
If a batch of product is certified by a qualified person in the EU for a specific market, in general there is no requirement to recertify the same batch. Examples of exceptions to this are if the product is further exported outside of the EU/EEA and reimported, or if the product undergoes a further manufacturing operation (e.g. repackaging) prior to release to the specific market.
- Is custom import required?
Custom requirements will not change with the implementation of Annex 21.
- Is financial import required?
The HPRA does not issue authorisations for financial importation (without physical importation). Local regulators should be contacted for any additional territory specific requirements.
Example 5
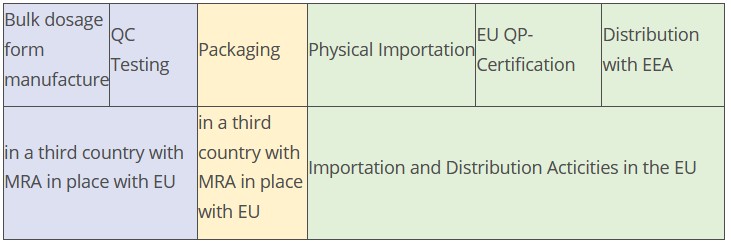
Is import testing required as there is an MRA with both the territories where bulk manufacturing and packaging takes place and the product is tested against the EU finished product specification?
Most of the MRA’s are bilateral in territorial applicability (i.e. applicable in the MRA state and in the EU and not for additional manufacturing steps in another MRA state) so in most cases import testing would be required.
Source:
„Annex 21 – Importation of Medicinal Products“ presentation by Ciara Turley, Senior GMP Inspector at HPRA, HPRA GMP Information Day, 4/5 May 2022, Dublin;
HPRA: GDP and GMP conferences
Do you have any questions or suggestions? Please contact us at: redaktion@gmp-verlag.de








