
Deviations Happen because People Make Mistakes...
8 min. reading time | by Thomas Peither
Published in LOGFILE 6/2023
In this feature we take look at the ‘black sheep’ of pharmaceutical production. As cute and charming as they may be in the animal world, in the world of GMP they can be rather disturbing.
They are the sand in the gears of smooth manufacturing that need to be identified, documented and investigated.
The trick here is not just to identify a single outlier, a black sheep, but also to recognise the grey animals that do not stand out at first glance.
What is a deviation? And what distinguishes it from a change?
Seemingly simple questions, but not so easy to answer at first glance. This is because there is no clear, generally applicable definition for the term ‘deviation’ in the various US and EU regulations.
To add to the confusion, different terms are often used: deviation, quality deviation, GMP deviation, product defect, OOS, discrepancy, atypical situation, non-conformity. Although these terms all suggest similar things, they are used to describe for very different events.
To avoid ambiguity and possible misunderstandings, each company must define what it means by a deviation. Generally speaking, a deviation is always unintentional, i.e. unplanned and retrospectively.
In contrast, a change is a planned and intentional modification, such as the addition or replacement of regulations, specifications, equipment, methods or processes. A change is therefore always prospective. It has a long-term or even permanent character.
In order to structure the internal handling of deviations, an overview of frequently used definitions of deviations is helpful. If these are as comprehensive as possible, relevant data from different areas can be collected together and evaluated comparatively.
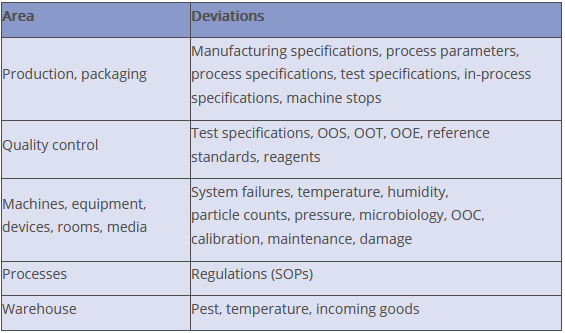
Where do deviations occur?
Deviations can occur in the area of production and packaging, for example in connection with
- manufacturing instructions,
- process parameters or specifications,
- test specifications for in-process controls or
- in-process specifications.
Process abnormalities or unexpected machine stops during production or packaging cannot be excluded.
Deviations can also occur during quality control, for example if test specifications are deviated from or if OOS, OOT or OOE results occur. And, of course, we are also aware of any deviations relating to machines, systems, equipment, rooms or media. Machines brak down from time to time and systems fail from time to time. Temperature, humidity, particle counts, pressure differences or calibration results may be outside the limits. Calibration or maintenance intervals are sometimes not adhered to, or there are deviations in microbiological monitoring, to name but a few.
Processes can also be prone to error, for example if SOPs are not followed exactly. Even warehouses are not immune to irregularities. Keywords: pest control or temperature fluctuations.
What types of deviations are there?
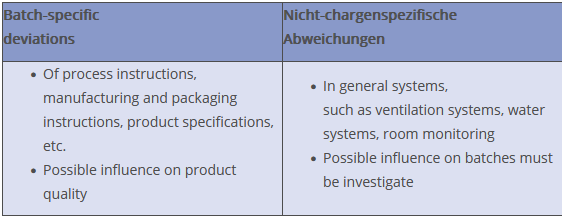
Basically, a distinction can be made between batch-specific and non-batch-specific deviations. The above mentioned events, which can occur during the manufacturing process, usually directly affect batches and may have an impact on product quality. This means: the safety, quality, identity, purity or content of the product is affected.
However, even in the case of non-batch-specific deviations, for example in the context of environmental monitoring in cleanroom Grade C, the possible influence on individual batches must always be assessed as part of the investigation.
A translated and shortened excerpt from episode 30 of the German webcast GMP & TEA ‘Deviations happen because people make mistakes...
Do you need more information about handling deviations?
In the GMP Compliance Adviser, you will learn, among other things, what is behind a deviation that should not actually exist, the planned deviation, what the regulatory requirements are for handling deviations, how deviations are handled in a GMP-compliant manner, and what all it all has to do with the qualified person.
Do you have any questions or suggestions? Please contact us at: redaktion@gmp-verlag.de








