
Highly Innovative Medicines: Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs) – Part 1
7 min. reading time | by Birte Scharf, PhD
Published in LOGFILE 8/2024
What are advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs)?
Advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs) are an innovative class of medicinal products characterised by the use of advanced technologies.They target the underlying genetic, cellular, or tissue-based abnormalities of diseases and thus offer the potential for cure or at least a long-term therapeutic benefit.
In contrast to conventional medicines, which often target symptoms, in some cases ATMPs even address the causes of disease, for example by correcting a causative genetic defect.
The field of ATMPs is developing rapidly and dynamically, driven by significant technological and scientific advances in biotechnology and medicine. These therapies, which include gene therapy, cell therapy, tissue engineering and their hybrid forms, offer new solutions to complex medical challenges. They open new possibilities for the treatment of diseases for which no or only inadequate therapy options exist to date. Hopes are high for advanced therapy medicinal products - whether for cancer, genetic disorders, or regenerative medicine.
The first part of this article outlines the definition of ATMPs and their categories. The second part provides an insight into the legal framework: the European Union guidelines on good manufacturing practice (GMP) specifically tailored to ATMPs (EU GMP Guideline Part IV) and the PIC/S GMP Guide Annex 2A. Furthermore, it includes a consideration of the challenges in ATMP manufacturing.
What are the ATMP categories?
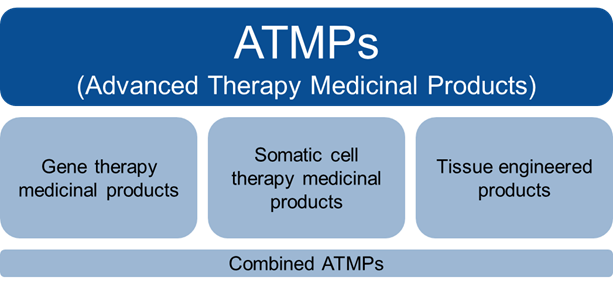
Figure 1 Categories of ATMPs
Gene therapy medicinal products:
Gene therapy involves the introduction of genetic material into a patient's cells or tissue to correct or compensate for abnormal genes responsible for the development of a disease. This can be achieved through a variety of delivery methods, including viral vectors, non-viral vectors or genome editing techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9.
Gene therapy holds immense potential for the treatment of a wide range of diseases, including genetic disorders, certain cancers and acquired diseases. By targeting the underlying genetic cause of diseases, gene therapy offers the possibility of achieving long-term or even permanent treatment results.
Example: In 2017, Luxturna® was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of hereditary retinal diseases caused by mutations in the RPE65 gene. Luxturna® delivers a functional copy of the RPE65 gene to the retinal cells, restoring the eyesight in people with the disease.
In addition to traditional gene therapies, there are also cell-based gene therapies, of which only CAR T-cell therapies (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell) have been approved by EMA or FDA. These involve genetically modifying a patient's own T-cells to express receptors that recognise and attack cancer cells. CAR T-cell therapy is currently mainly used to treat certain types of blood cancer such as leukaemia and lymphoma, but FDA also approved the first T-cell therapy for a solid tumor last month.
Somatic cell therapy medicinal products:
Cell therapy utilises the regenerative capacity of living cells to restore or enhance cell function in diseased or damaged tissues. Cells may originate from the patient (autologous) or from a donor (allogeneic) and are usually administered by injection or infusion. These cells can be manipulated or modified ex vivo prior to administration to target specific disease mechanisms.
Example: Alofisel® is a somatic cell therapy consisting of stem cells derived from the fat tissue of a healthy donor. This product is used to treat complex anal fistulas in adults with Crohn's disease. The stem cells are injected into the fistulas, reduce inflammation, promote tissue growth, leading to healing and closure of the fistulas.
Tissue engineered products:
Tissue engineering combines cells, biomaterials and biochemical factors to create functional tissue substitutes for transplantation or regeneration. It involves the construction of three-dimensional structures that mimic the structure and function of native tissue and promote tissue repair or regeneration. Tissue engineering has the potential to address a wide range of medical needs, including repairing damaged tissue, replacing organs and promoting tissue regeneration. Applications of tissue engineering include skin grafts for burn patients, cartilage repair in orthopaedic surgery and bioengineered organs for transplantation.
Example: In orthopaedics, tissue engineered cartilage constructs are being developed as an alternative to conventional cartilage repair procedures for diseases such as osteoarthritis. These constructs, which consist of chondrocytes embedded in biocompatible scaffolds, are designed to regenerate damaged cartilage and restore joint function.
Combined ATMPs:
Some therapies combine elements of gene therapy, cell therapy and tissue engineering to comprehensively address complex medical challenges. These combined ATMPs use multiple approaches to synergistically target different aspects of disease pathophysiology.
Example: Engineered autologous skin substitutes combine elements of tissue engineering and cell therapy to treat severe burns and chronic wounds. These constructs consist of patient-derived skin cells cultured on biocompatible scaffolds and promote wound healing and tissue regeneration.
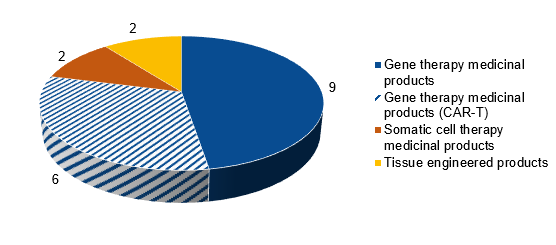
Figure 2 ATMPs authorised according to the EMA (19 March 2024)
Read the next LOGFILE to find out what regulatory requirements need to be met and what challenges are involved in the manufacture of ATMPs.
Do you have any questions or suggestions? Please contact us at: redaktion@gmp-verlag.de








