
GMP/GDP Requirements for Different Storage Areas
Excerpt of the GMP & TEA
8 min. reading time | by Thomas Peither
Published in LOGFILE 27/2023
General requirements
Adequate size and lighting of all areas where medicinal products, starting materials and packaging materials are stored is essential for the proper performance of operations.
Access to storage areas must be clearly regulated and protected.
Both EU GMP and EU GDP guidelines emphasise the importance of storage protected from the weather. Goods should therefore always be received inside the warehouse. Only in exceptional cases is it acceptable to do this outside under a canopy.
In addition, the areas for receiving and shipping should be separated from each other.
If there is little space, additional organisational measures are necessary, for example decoupling delivery and picking processes or separating the corresponding areas at least with mobile partition walls or barrier chains.
Dedicated storage areas
Rejected, blocked and returned commercial material must be marked "blocked" and stored in a separate blocked storage area accessible only to authorised personnel.
Dedicated storage areas are also required for highly potent substances. According to the WHO-GSDP (Good Storage and Distribution Practices for Medicinal Products) guideline, this also applies to radioactive materials, narcotics, substances with a risk of misuse or with a risk of fire or explosion, hazardous materials or sensitive substances.
Special requirements for the storage of critical materials are defined, among others, in national regulation on narcotics and the hazardous substances. Printed packaging material is also considered critical from a GMP point of view; special climate-controlled intermediate storage may be required for conditioning for the packaging process.
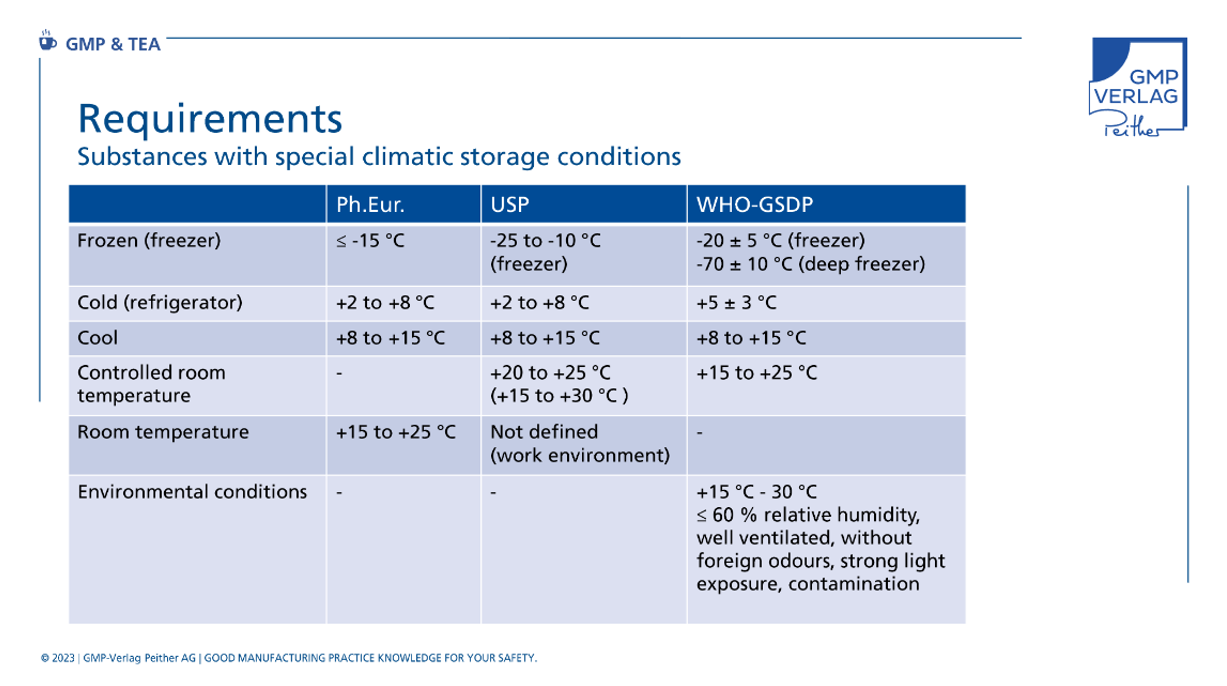
Dedicated storage is required for substances with deviating climatic storage conditions. Often, this requires special cold storage facilities or storage areas with special specifications for relative humidity. Basic specifications for this can be found in the EU GMP guidelines as well as in the GDP guidelines and in 21 CFR 211.
Storage instructions based on stability data shall be considered as target values for storage conditions in order to be able to adopt, for example, expiry dates. The storage temperature specifications stated on the packaging of the finished product shall be selected in accordance with the EMA Guideline on Declaration of Storage Conditions. Relevant pharmacopoeias and the WHO-GSDP provide storage instructions for specific temperature ranges.
But be careful! Terms such as "deep-frozen" or "room temperature" can mean different temperatures depending on the source. The following comparison of the terms and requirements in the various regulations can be helpful here.
This article is a shortened and translated excerpt from the 32nd episode of our GMP & TEA webcast .
Do you have any questions or suggestions? Please contact us at: redaktion@gmp-verlag.de








